- Mechanism: Rising global temperatures → increased melt of glaciers, ice caps, ice sheets.
- Result: Meltwater flows to oceans → global sea level rise. [NASA_2022]
- Note: Melting sea ice (e.g., Arctic) does NOT contribute significantly to sea level rise as its volume is already displaced (Archimedes' Principle).
Global Sea Level Rise: Causes, Effects, and Solutions
Pinak Paliwal, Natalie Zhou
Leland High School
AP Environmental Science - Ms. Biswas
Due Date: May 19th, 2025
Introduction: Historical Timeline
-
Late 19th Century: Early Observations
- Scientists began measuring sea levels using tide gauges.
- Data revealed a gradual rise in sea level over time.
-
Late 20th Century: Public Awareness and Scientific Breakthroughs
- Widespread public knowledge emerged.
- Improved scientific understanding linked global warming to melting ice sheets and thermal expansion of seawater.
-
1992: Technological Advancement
- Launch of TOPEX/Poseidon, a joint satellite mission by NASA and France.
- Provided precise, consistent global sea level measurements, which confirmed both sea level rise and the acceleration of the rate at which the global sea level was rising.
- Continuous monitoring (30-year record) provides crucial data. [Carlowicz_2022]
Understanding Sea Level Rise
-
Current Understanding:
- Largely attributed to human-driven climate change.
- Key Mechanisms: Thermal expansion, melting of land-based ice (glaciers, ice caps). [NASA_2022]
As Dr. Sophie Nowicki, a member of NASA's Sea Level Change Team, states: "Sea-level rise has happened, and it will continue to rise. Our coasts are going to change. They are changing. So we need to find a way to adapt". This acknowledgment of the inevitability of some degree of sea level rise emphasizes the importance of both mitigation and adaptation strategies [Brennan_2025].
Present Day: Human Impact on Climate Change
Sea level rise is now largely attributed to human-driven climate change. Key human contributions include:
- Burning Fossil Fuels: Coal, oil, and natural gas release CO2, leading to global warming.
- Industrial Activities: Factories and manufacturing plants emit CO2, methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O - GWP of 250+).
- Deforestation: Reduces Earth’s ability to remove CO2 via photosynthesis; stored carbon is released.
-
Agriculture:
- Rice Paddies: Anaerobic conditions for bacterial decomposition of organic material produce methane.
- Livestock: Animals like cows, sheep, and goats produce methane through enteric fermentation (burping).
- Waste Decomposition: Anaerobic decomposition in landfills releases methane.
-
Man-made Chemicals:
- CFCs (Chlorofluorocarbons): Used in aerosols and refrigerants; deplete the ozone layer and have high GWPs (e.g., CFC-12 GWP ~11,000).
- HFCs (Hydrofluorocarbons): Replacements for CFCs, but also potent greenhouse gases (e.g., HFC-23 GWP ~12,500).
- Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol aims to phase out HFCs.
These activities increase greenhouse gas concentrations, trapping more heat and causing global warming, which in turn drives thermal expansion of oceans and melting of land-based ice.
Causes: Thermal Expansion
- Ocean Heat Absorption: Oceans absorb ~90% of excess heat from increased greenhouse gases. [Paddison_2025]
-
Expansion:
- Warming water expands, increasing ocean volume.
- Result: Global sea level rise.
-
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion:
- Varies (temperature, salinity).
- General estimate: 1°C ocean warming → 0.5-1 meter sea level rise (not uniform).
- 2024 Findings: Thermal expansion ~2/3 of global sea level rise (reversal from prior years where ice melt dominated). [Jacobo_2025]
- Josh Willis (NASA): Ocean continues to rise, rate increasing, despite switch in dominant cause.
Causes: Melting of Land-Based Ice

Melting Ice Sheets: A major contributor to global sea level rise. [Miller_2018]
Mechanics: Positive Feedback Loop - Permafrost Thaw
The melting of permafrost creates a dangerous positive feedback loop, accelerating global warming:
- Initial Warming: Rising global temperatures begin to thaw permafrost (frozen soil found in Arctic and high-altitude regions).
-
Greenhouse Gas Release:
- Thawing permafrost releases vast amounts of trapped greenhouse gases.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2) is released from the decomposition of previously frozen organic matter.
- Methane (CH4), a more potent greenhouse gas in the short term, is released by anaerobic bacteria decomposing organic matter in waterlogged, thawed soils.
- Increased Atmospheric GHGs: The released CO2 and CH4 add to the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Enhanced Greenhouse Effect: More greenhouse gases trap more heat, leading to further increases in global air temperatures.
- Accelerated Thawing: Warmer air temperatures cause more permafrost to thaw, releasing even more greenhouse gases.
This cycle continues, with each step reinforcing the next, significantly amplifying the effects of initial warming and contributing further to the melting of glaciers and polar ice caps, thus exacerbating sea level rise.
Ice Loss: Greenland & Antarctica
Direct measurements reveal alarming trends [Lindsey_2023]:
- Greenland Ice Sheet: Loss increased seven-fold (34 to 247 billion tons/year, 2012-2016).
- Antarctic Ice Sheet: Loss nearly quadrupled (51 to 199 billion tons/year, 1992-2001 vs 2012-2016).
-
Projections (NASA's ISMIP, Sophie Nowicki):
- Current emission rates: Greenland & Antarctica could add >15 inches (38 cm) by 2100.
- This is beyond already "locked-in" rise. [Ramsayer_2020]
Effects: Impact on Human Populations (Part 1)
-
Primary Impacts (Coastal & Global):
- Population displacement
- Infrastructure damage
- Freshwater contamination
-
Direct Impact: Increased coastal flooding (frequency &
severity).
- Example: Louisiana coastline (forced relocation).
- High-risk US cities: Miami, New York, New Orleans (need investment in protection/adaptation).
-
Health Risks from Contaminated Water:
- Untreated sewage entering freshwater can create low-oxygen conditions perfect for disease-carrying vectors and bacteria.
- Cholera: Spreads in untreated freshwater, causing severe diarrheal disease.
- Cryptosporidiosis: Caused by a parasite found in sewage, resistant to chlorine, making water treatment difficult.
Effects: Impact on Human Populations (Part 2)
-
Freshwater Contamination (Continued):
- Saltwater intrusion or untreated wastewater.
-
Airborne pollutants deposited into freshwaters (rain/wind):
- Mercury: From coal combustion, converts to toxic methylmercury, bioaccumulates in aquatic food chains.
- Dioxins: From industrial burning, bioaccumulate in fish, carcinogenic.
- Threatens drinking water and agriculture (salinization).
-
Chain Reactions from Contamination:
- Eutrophication: Excess nutrients from sewage/runoff cause algal blooms, depleting oxygen and harming aquatic life.
- Bioaccumulation & Biomagnification: Toxins like mercury and dioxins concentrate up the food chain, posing risks to humans consuming contaminated seafood.
- Outbreaks of diseases like cholera become more likely in flooded regions with compromised sanitation.
-
Economic Costs:
- US flooding: ~$500 billion annually (infrastructure, lost revenue, insurance). [Paddison_2025]
- IMF: Decreased property values, difficulty securing mortgages.
Bottom line: Freshwater contamination from sea level rise causes chain reactions harming human health and water usability for decades.
Visualizing Human Impact: Flooding (Alabama)
This image illustrates the devastating impact of flooding on communities, such as this neighborhood in Alabama. It underscores the urgent need for improved infrastructure and comprehensive climate strategies to mitigate such events and protect vulnerable populations.
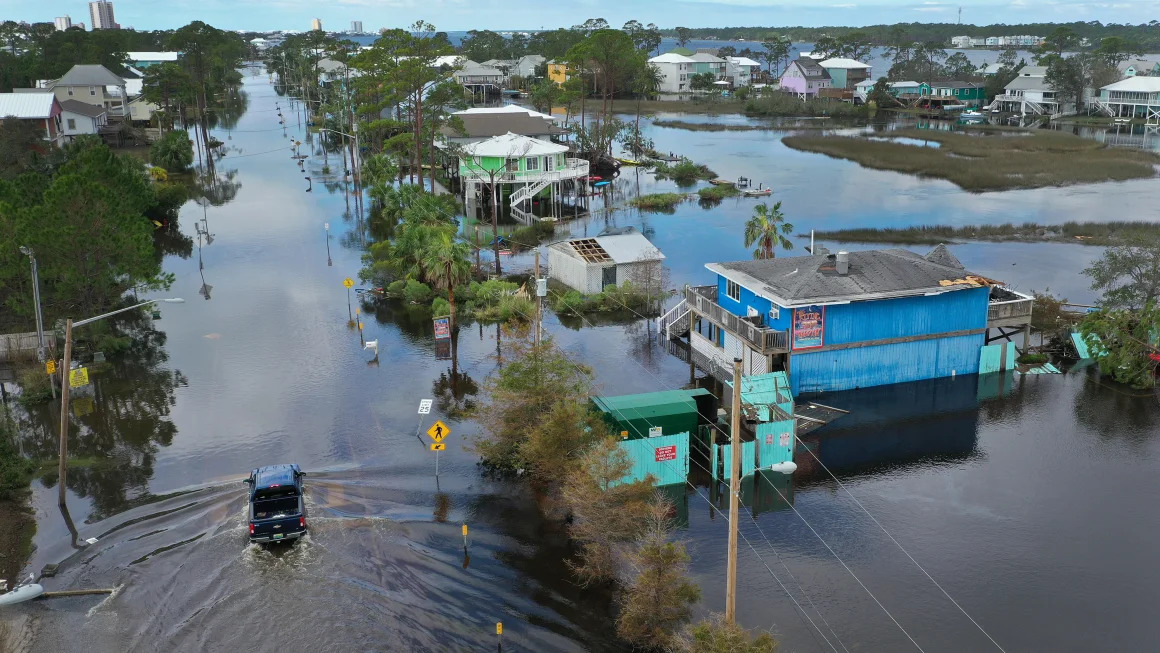

Flooding in Gulf Shores, Alabama, post-Hurricane Sally in 2020. Illustrates devastating impact on communities and the urgent need for infrastructure improvements and climate strategies. [Ramirez_2022]
Visualizing Human Impact: Flooding (Fiji)
The image depicting the impact on Fijian villagers highlights the severe consequences of sea level rise, particularly for low-lying island nations. Forced relocation is becoming a reality for many, emphasizing the critical need for global climate action and support for affected communities.
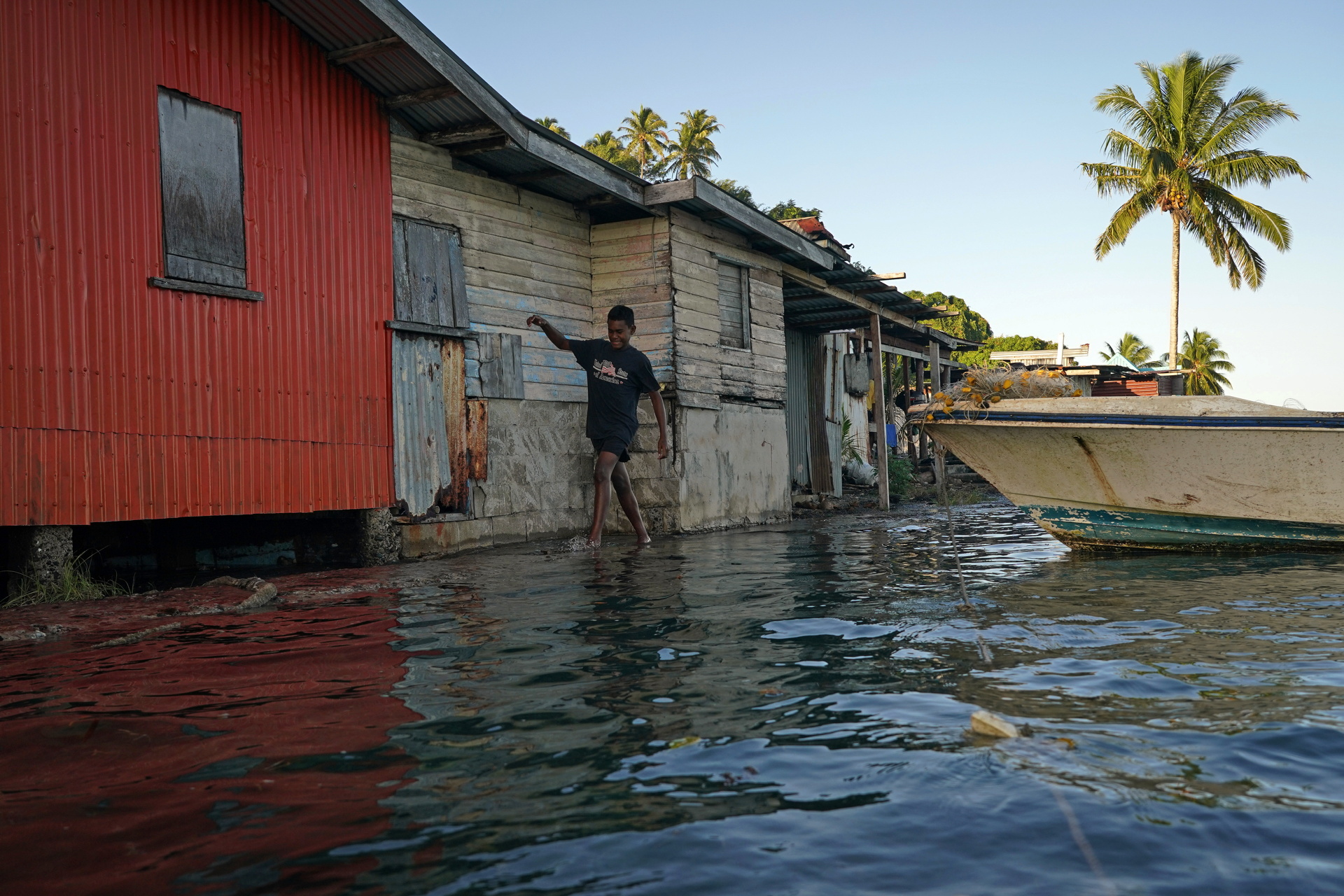
Impact on Fijian Villagers: Shows forced relocation in low-lying island nations, highlighting the critical need for climate action. [Needham_2022]
Effects: Impact on Biodiversity (Part 1)
- Key Impacts: Habitat loss, increased salinity, altered coastal ecosystems.
- Vulnerable Species: Coastal and island species.
- At-Risk Ecosystems: Mangroves, salt marshes, coral reefs (coastal squeeze).
-
Susceptible Species: Limited ranges, specialists. [Noe_Krauss_2014]
- Example: Bramble Cay Melomys (extinct 2019 due to habitat loss).
- Sea turtles: Nesting site loss by 2050 (e.g., Florida, Cuba).
- Coastal Wetlands & Estuaries: Flooding increases runoff of nitrogen and phosphorus, causing algal blooms and oxygen dead zones.
Effects: Impact on Biodiversity (Part 2)
-
Saltwater Intrusion into Freshwater Ecosystems:
- Reduces plant water uptake and disrupts root function.
- Soil becomes saltier (hypertonic relative to plant cells), causing water to move out of roots via osmosis (plasmolysis), leading to wilting and plant death.
- Damages soil structure, affects nutrient availability, and impacts carbon storage.
-
Blue Carbon Ecosystems:
- Rising seas can drown ecosystems like salt marshes, seagrass beds, and mangroves if they can't build sediment or grow upward fast enough.
- Death of these plants reduces their ability to trap and store significant amounts of CO2 (blue carbon).
-
Further Examples of Susceptible Species:
- Coral reefs: ~80% warm-water reefs to disappear with few degrees Celsius warming.
- Mediterranean wetland birds: >1/3 coastal wetlands submerged by 2100. [Mouterde_2024]
- Polar bears: Threatened by melting sea ice (hunting).
-
Consequences of Reduced Biodiversity:
- Decreased marine food web functionality (fisheries affected).
- Altered nutrient cycles.
- Impacted ecosystem services (storm protection, water purification, carbon sequestration) due to mangrove/wetland decline.
Effects: Impact on the Global Community (Part 1)
- Global Crisis: Disproportionate impact on coastal communities & small island nations.
- Existential Threat: Tuvalu, Marshall Islands, Kiribati (low-lying geography).
As Lionel Aingimea, President of Nauru, stated: "Sea level rise is not only about an existential threat to our small and low-lying island. Climate change also threatens an economic Armageddon if the tuna fishery disappears". [Needham_2024]
Effects: Impact on the Global Community (Part 2)
- Existential Crisis (cont.): Kiribati, Tuvalu, Marshall Islands due to low average altitude. [Canagarajah_2024]
- Adaptation Costs (Small Island Nations): World Bank estimates ~$10 billion needed (significant GDP fraction).
- Developed Nations' Strategies: US (Pacifica seawalls). [Duggan_2025]
-
Economic Impacts (IMF):
- Decreased property values.
- Difficulty securing mortgages.
- US Flooding Costs: ~$500 billion annually (infrastructure, lost revenue, insurance).
Recent Sea Level Rise Statistics (Part 1)
- Accelerating Pace Confirmed.
- Total Rise (since 1880): 21-24 cm (due to ice melt & thermal expansion).
- 2023 Status: Global mean sea level 101.4 mm (3.99 inches) above 1993 levels (highest in satellite record).
-
Rate Increase:
- 2006-2015: 0.14 inches (3.6 mm)/year.
- Most of 20th century: 0.06 inches (1.4 mm)/year. [Lindsey_2023]
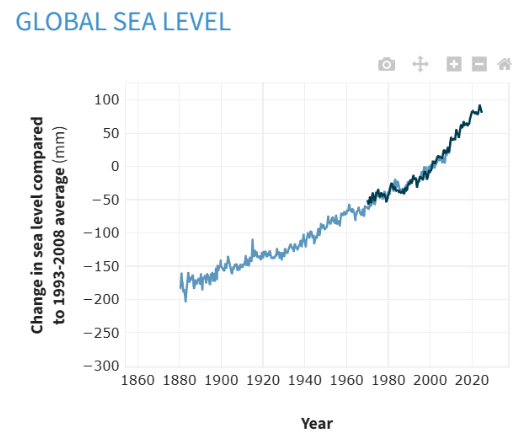
The overall change in Global Sea Level vs Year.
Recent Sea Level Rise Statistics (Part 2)
- Alarming Acceleration: Concerns scientists and coastal planners.
-
Regional Increases (1993-2023, Satellite Data):
- 15-20 cm (6-8 inches) in some ocean basins.
- Notably: Southeastern US, Southeast Asia. [Carlowicz_2022]
- Rate Doubled: Annual sea level rise rate more than doubled since 1993. [Jacobo_2025]
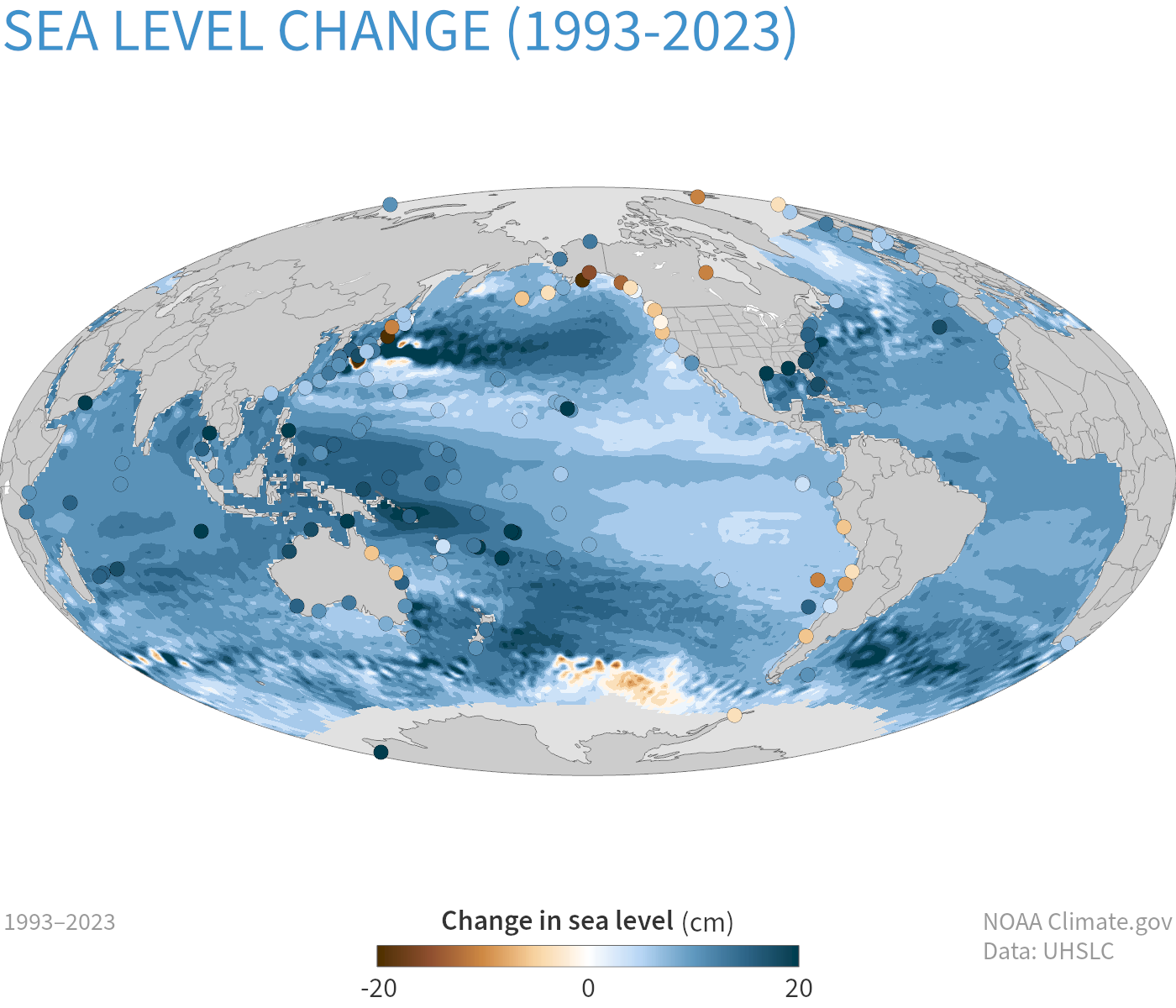
The change in sea level around the world.
Recent Sea Level Rise Statistics (Part 3)
-
Projected Impact by 2100 (High Emissions, Limited Adaptation):
- Map shows people on land below sea level.
-
Highest Risk Regions (10-50 million affected):
- China, India, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Southeast Asia.
- Especially densely populated, low-lying coastal areas.
-
Other Affected Regions (1-9 million affected):
- US, Brazil, EU, parts of Africa.
- Map Underscores: Significance of global sea level rise and urgent need for mitigation.
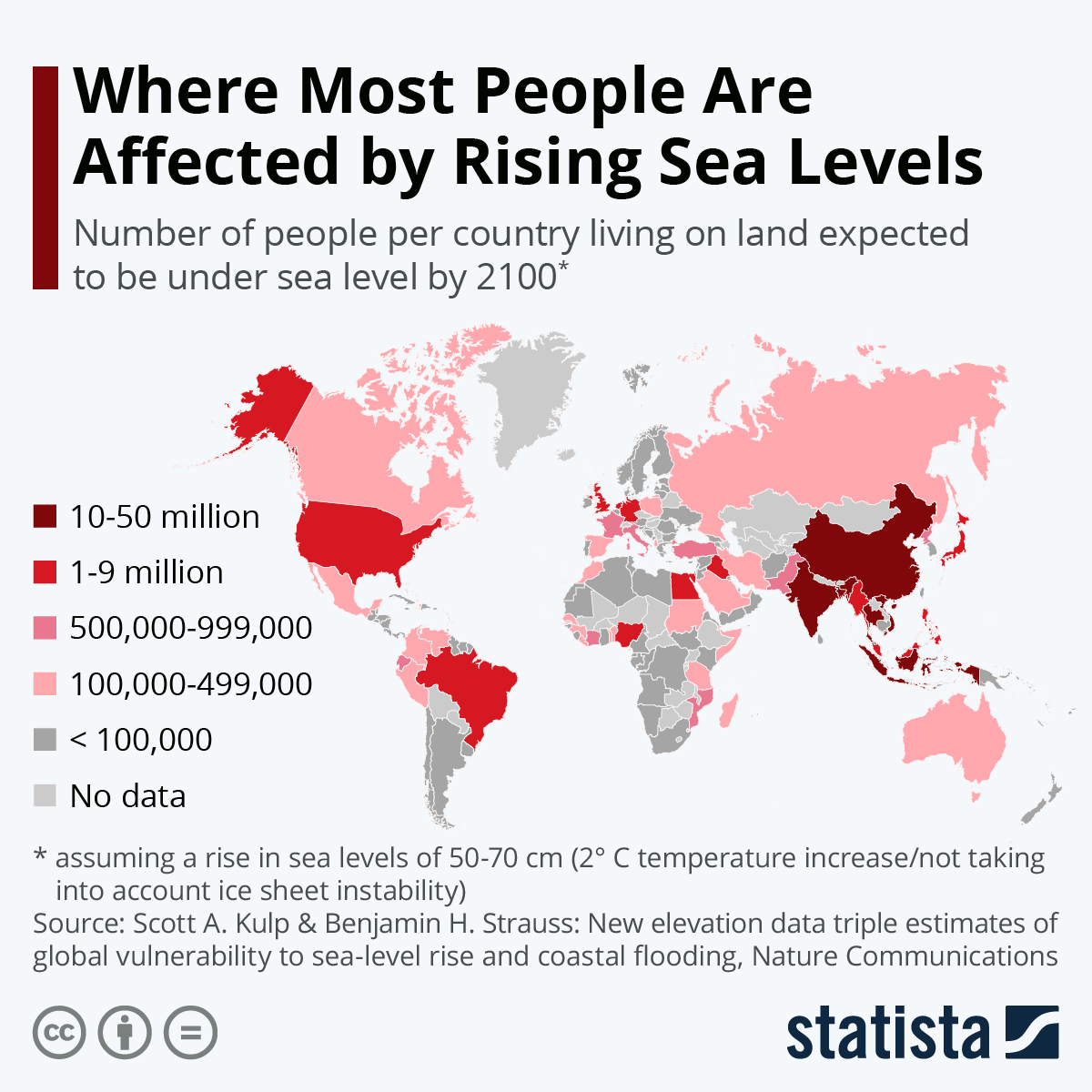
A global map showing where people will be most affected.
Future Projections: SSP Scenarios
- Projections vary by Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs).
- SSPs show different sea level rise possibilities by 2100 based on global cooperation.
- Consequences differ dramatically based on emission reduction efforts. [Nauels_Rogeli_Schleussner_2017]
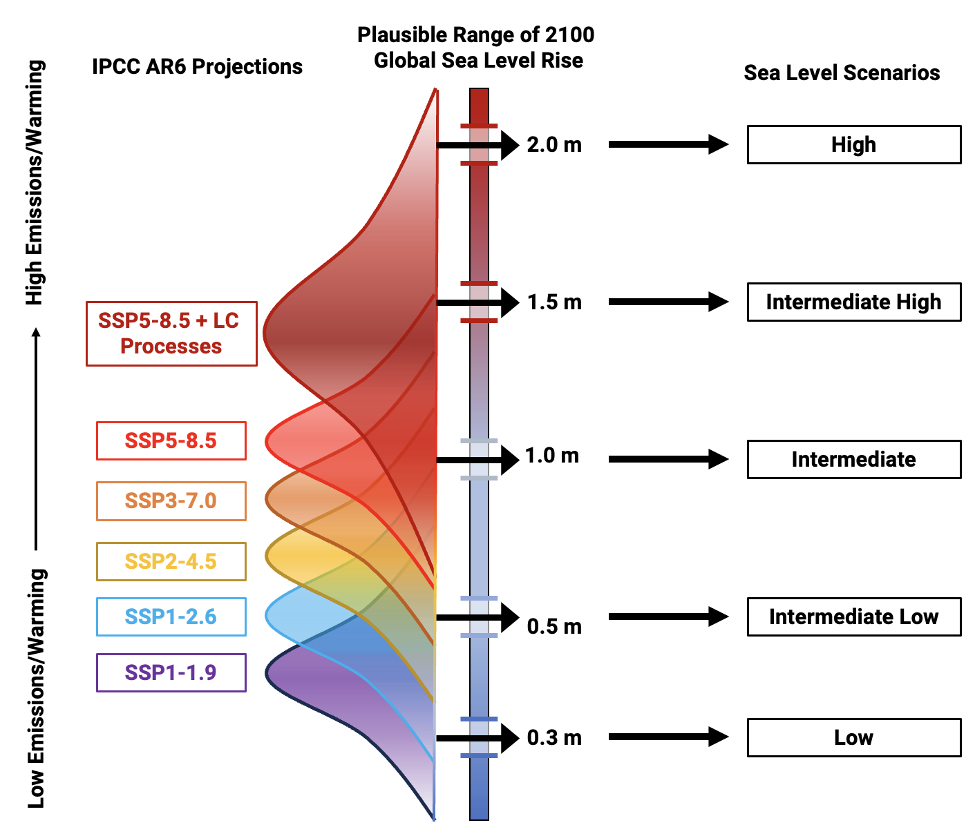
A sample SSP Diagram illustrating potential sea level rise by 2100.
Interpreting SSP Scenarios
An interpretation of the SSP Diagram for 2100:
- Low scenario: 1 foot (unlikely, assumes current rates continue)
- Intermediate Low: 1.6 feet (excludes rapid ice sheet loss)
- Intermediate: 3.3 feet (includes small chance of rapid ice melt)
- Intermediate High: 4.9 feet (assumes high warming continues)
- High: 6.6 feet (worst-case with extreme ice sheet instability)
- Minimum Rise: Even with low emissions, likely at least 1 foot (0.3m) above 2000 levels by 2100. [Lindsey_2023]
The core message is that lowering our carbon footprint is crucial to mitigate damage, especially for at-risk communities.
Solutions: Individual Actions (Part 1)
-
Most Effective: Reduce personal carbon footprint.
- Why: Greenhouse gases drive warming & sea level rise.
-
Practical Steps: [Cho_2018]
- Transport: Walk, bike, public transport (vs. driving).
-
Diet: Reduce meat and dairy consumption.
- The 10% rule in ecology means producing meat requires significantly more land and resources than plant-based foods for the same energy.
- Fertilizers for animal feed crops emit nitrous oxide (N2O).
- Fuel for farm machinery and transport burns fossil fuels.
- Land conversion for pasture/feed releases sequestered carbon.
-
Energy Conservation:
- Unplug electronics and turn off lights when not in use.
- Switch to energy-efficient appliances.
- Insulate homes to reduce heating/AC needs.
- Less demand for electricity means less fossil fuel burning by power plants.
-
Conscious Consumption:
- Buy fewer, higher-quality, longer-lasting items.
- Recycle and repurpose wherever possible.
Solutions: Individual Actions (Part 2)
-
Encourage Others & Raise Awareness:
- Discuss sustainable habits on social media (e.g., Instagram, TikTok to reach younger generations), with friends/family.
- Educate on the carbon impact of daily choices.
- Arrange carpooling or promote community sustainable initiatives.
- Utilize online forums to spread awareness and share tips.
-
Obstacles to Adoption:
- Inconvenience or perceived expense of lifestyle changes.
- Time commitment for public transport vs. driving.
- Cost/familiarity challenges with plant-based diets.
-
Overcoming Obstacles:
- Education on the long-term environmental and economic impacts of inaction.
- Community support for accessible and affordable sustainable choices.
- Highlighting co-benefits (e.g., health improvements from active transport/changed diet).
Solutions: Governmental & International Actions (Part 1)
-
Federal Investment in Renewable Energy:
- Actions: Increase subsidies for clean energy (solar, wind, hydro, geothermal), fund job transition programs for workers in non-renewable sectors.
- Goal: Drastically reduce fossil fuel emissions.
-
Leadership by Major Emitters (US, China, EU):
- Fund and incentivize solar, wind, hydro, geothermal projects to accelerate the green energy transition.
-
Policy Mechanisms:
- Enact federal legislation and executive orders prioritizing climate action.
- General Call: All countries to increase subsidies/incentives for clean energy transition and implement carbon pricing mechanisms.
Solutions: Governmental & International Actions (Part 2)
As Isabella Lövin emphasized, international cooperation is essential: "The ocean knows no borders – you don't have to use your passport – so we need to work along the lines of the natural marine ecosystems. Neighbouring countries must work together" [Myers_2020].
-
Potential Obstacles:
- Resistance from fossil fuel industries and lobbying efforts (delaying pro-renewable legislation).
- National reluctance: Prioritizing short-term economic gains over long-term climate goals and sustainability.
- Geopolitical tensions hindering collaborative efforts.
-
Overcoming Challenges:
- Strong political leadership and commitment to climate targets.
- Sustained public pressure and advocacy from civil society.
- International accountability mechanisms and transparent reporting (e.g., under the Paris Agreement).
- Highlighting economic opportunities in green transitions.
Solutions: Engineering Actions (Part 1)
Innovative engineering solutions are being explored to adapt to and mitigate sea level rise:
-
Large-Scale Seawater Storage Systems:
- Concept: Pumping seawater into inland reservoirs or underground caverns.
- Status: Mostly theoretical; no large-scale real-world implementations yet.
- Challenges: Massive energy requirements for pumping, extremely high costs, potential environmental impacts (e.g., land use, seismic risks, brine disposal).
- Feasibility: Currently low due to practical and environmental concerns.
-
Coastal Barriers (Hard Defenses):
- Examples: Seawalls, levees, storm surge barriers, breakwaters.
- Function: Physically block rising seas and storm surges to protect coastal infrastructure and communities.
-
Real-World Examples:
- Netherlands: Maeslantkering storm surge barrier (steel gates, cost ~€450 million).
- Venice, Italy: MOSE project (mobile floodgates, super-duplex stainless steel, cost ~€6 billion).
- Feasibility: Significantly more feasible than large-scale storage, especially for protecting high-value areas or nations with low altitudes.
- Costs: Moderate to very high, depending on scale, materials, and complexity.
- Considerations: Can cause coastal squeeze, impact sediment flow, and may not be suitable for all coastlines.
Solutions: Engineering Actions (Part 2)
-
Floating Infrastructure:
- Concept: Building homes, roads, and entire neighborhoods on buoyant platforms that rise and fall with water levels.
- Examples: Floating homes in Amsterdam (Netherlands), various pilot projects globally.
- Function: Allows communities to adapt to changing water levels without costly land reclamation or relocation.
- Feasibility: Decently feasible, especially for smaller communities or specific infrastructure components. Ideal for areas prone to frequent flooding or with limited land.
- Costs: Moderate to high, but potentially cheaper in the long run than rebuilding flood-damaged, ground-anchored infrastructure.
- Benefits: One of the more promising long-term adaptive solutions, offering flexibility as structures can be moved or reconfigured.
-
Other Engineering Approaches:
- Beach nourishment and dune restoration (soft defenses).
- Elevating existing infrastructure.
- Developing advanced drainage systems.
Engineering solutions offer adaptive capacities but must be combined with strong mitigation efforts (reducing emissions) for long-term sustainability. Each solution has its own economic, environmental, and social trade-offs.
References
- Brennan, P. (2025, April). Scientist interview: Sophie Nowicki. NASA. https://sealevel.nasa.gov/news/234/scientist-interview-sophie-nowicki/
- Canagarajah, S. (2024, June). Climate change: Sids. World Bank Blogs. https://blogs.worldbank.org/en/climatechange/four-things-you-should-know--climate-change---small-island-devel
- Carlowicz, M. (2022, November). Tracking 30 years of sea level rise. NASA. https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/150192/tracking-30-years-of-sea-level-rise
- Cho, R. (2018, December). The 35 easiest ways to reduce your carbon footprint. State of the Planet. https://news.climate.columbia.edu/2018/12/27/35-ways-reduce-carbon-footprint/
- Duggan, T. (2025, May). California Coastal Commission balks at seawalls. it made .... San Francisco Chronicle. https://www.sfchronicle.com/california/article/pacifica-seawall-coastal-commission-20311371.php
- Jacobo, J. (2025, March). Global sea level rose faster than expected in 2024, according to NASA analysis. ABC News. https://abcnews.go.com/International/global-sea-level-rose-faster-expected-2024-nasa/story?id=119795389
- Lindsey, R. (2023, August). Climate change: Global sea level. NOAA Climate.gov. https://www.climate.gov/news-features/understanding-climate/climate-change-global-sea-level
- Miller, B. (2018, March). Satellite observations show sea levels rising. CNN. https://www.cnn.com/2018/02/12/world/sea-level-rise-accelerating/index.html
- Mouterde, P. (2024, May). Mediterranean wetland birds threatened by rising sea levels. Le Monde.fr. https://www.lemonde.fr/en/environment/article/2024/05/18/mediterranean-wetland-birds-threatened-by-rising-sea-levels_6671795_114.html
- Myers, J. (2020, June). Quotes on the future of our ocean from queen Noor of Jordan, Marc Benioff and more. World Economic Forum. https://www.weforum.org/stories/2020/06/quotes-ocean-future-environment-climate-change/
- NASA. (2022, February). Overview. NASA. https://sealevel.nasa.gov/understanding-sea-level/global-sea-level/overview/
- Nauels, A., Rogeli, J., & Schleussner, C.-F. (2017, October). Linking sea level rise and socioeconomic indicators under the shared.... Climate Analytics. https://climateanalytics.org/publications/linking-sea-level-rise-and-socioeconomic-indicators-under-the-shared-socioeconomic-pathways
- Needham, K. (2022, August). Rising sea levels are forcing Fiji’s villagers to relocate. Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/investigates/special-report/climate-change-fiji-sealevels/
- Needham, K. (2024, September). Sinking Tuvalu fights to keep maritime boundaries as sea levels rise | reuters. Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/investigations/sinking-tuvalu-fights-keep-maritime-boundaries-sea-levels-rise-2024-09-24/
- Noe, G., & Krauss, K. (2014, November). Sea level rise and nutrient cycling in coastal wetlands. USGS. https://www.usgs.gov/news/sea-level-rise-and-nutrient-cycling-coastal-wetlands
- Novenario, C. (2022, October). 5 reasons why floating development is set to take the world by storm. Global Center on Adaptation. https://gca.org/5-reasons-why-floating-development-is-set-to-take-the-world-by-storm/
- Paddison, L. (2025, May). Global sea levels are rising faster and faster. it spells catastrophe for coastal towns and cities. CNN. https://www.cnn.com/2025/05/09/climate/sea-level-rise-melting-ice-sheets
- Ramirez, R. (2022, February). US sea levels will rise rapidly in the next 30 years, New Report shows. CNN. https://www.cnn.com/2022/02/15/us/us-sea-level-rise-report-noaa-climate/index.html
- Ramsayer, K. (2020, September). Emissions could add 15 inches to sea level by 2100, NASA-led study finds – climate change: Vital signs of the planet. NASA. https://climate.nasa.gov/news/3021/emissions-could-add-15-inches-to-sea-level-by-2100-nasa-led-study-finds/